What is Compatibility Testing? Example Test Cases Included!
March 18th, 2024

Imagine pouring hours into perfecting your software application only to discover it crashes on certain devices or displays bizarre errors in specific browsers.
Compatibility issues are a developer’s hidden nightmare, capable of ruining user experiences and damaging your product’s reputation.
That’s where compatibility testing comes in. It’s your shield against these frustrations, ensuring your software functions seamlessly across the ever-changing landscape of operating systems, hardware, and browsers.
Let’s dive deeper into why compatibility testing is crucial and how it can empower you to deliver an exceptional experience to every user.
What Is Compatibility Testing?
Compatibility testing is a non-functional testing method primarily done to ensure customer satisfaction. This testing process will ensure that the software is compatible across operating systems, hardware platforms, web browsers, etc.
The testing also serves as validation for compatibility requirements that have been set at the planning stage of the software. The process helps in developing software that has the ability to work seamlessly across platforms and hardware without any trouble
Compatibility testing is conducted in mobile applications for the following reasons:
- This testing is performed to make sure that the final app product performs as expected on various mobiles and devices of different make and models
- This is a type of non-functional testing whose main aim is to check the compatibility of applications with browsers, mobiles, networks, databases, operating systems, hardware platforms, etc.
- Through this method, the behavior of a mobile app in different environments can be analyzed
- With this testing, a tester can detect any error before the final launch of the mobile application in the market
- This testing confirms that all the necessary requirements set by the developer and end-user have been met by the app
- Helps to create top-notch bugs free applications, which helps in accelerating the reputation of the firm and moving the business towards success
- Dynamic testing ensures the stability and workability of the mobile app before it finally gets released in the market
When to Perform Compatibility Testing:
Compatibility testing is an important phase in the software testing process after a company has created what it feels can be termed a ‘stable’ version of its software that reflects the intended behavior of end users.
This stage runs after other testing efforts like alpha and acceptance testing that emphasize the integrity of overall stability and feature-based bugs.
Compatibility testing focuses on issues of compatibility between the software and other environments.
Early compatibility testing can make checks inoperative.
This is why initial compliance tests become irrelevant as minor changes are made to the system in later stages of development that can significantly alter the compatibility test result.
When Software Compatibility Testing is Unnecessary:
In the intricate dance of software development, compatibility testing often takes center stage, ensuring your application performs harmoniously across various platforms and environments.
However, there are moments—specific scenarios—where the spotlight dims on this critical testing phase. Let’s explore these situations with clarity and consideration.
Highly Constrained Environments
- Controlled Configuration: Developing for a single, well-defined setup (OS, hardware, browser) means predictability reigns supreme. With no wild cards in the deck, compatibility testing might seem like an unnecessary encore.
Insignificant Internal Applications
- Small, Controlled User Base: For internal tools used within a standardized technological landscape, extensive compatibility testing could be overkill. Yet, a cursory glance to ensure smooth operation on key configurations can prevent unforeseen hiccups.
Proofs of Concept (POCs) and Prototypes
- Core Functionality Focus: In the embryonic stages of development, the aim is to showcase the idea’s viability, not its adaptability across diverse platforms. Full-scale compatibility testing can wait until the foundation solidifies.
Extreme Time Constraints
- Prioritization is Key: When deadlines loom like towering wave, some compatibility tests may be jettisoned to stay afloat. However, prioritizing tests for the most critical platforms ensures the ship doesn’t sink before reaching port.
Important Considerations and Caveats
“Unnecessary” Doesn’t Mean “Ignored”
- Basic Compatibility Checks: Even in scenarios where extensive testing seems redundant, a few strategic tests can illuminate major issues before they darken your doorstep.
Market and User Expectations
- Audience Needs: The scale of compatibility testing should align with your software’s intended reach. Niche applications may navigate narrower channels, while consumer-facing software sails the open seas of platform diversity.
Long-term Costs
- Future-proofing: Skipping compatibility testing might streamline your immediate journey, but beware of icebergs ahead—support costs, technical debt, and user dissatisfaction can rapidly accumulate.
Always Proceed with Caution
Opting to dial back on compatibility testing isn’t a decision to be made lightly. Consider the landscape ahead, chart your course with these factors in mind:
- Scope of the Project: The application’s size and complexity can guide the extent of necessary testing.
- Target Market: Understanding the diversity of your user base helps tailor your testing strategy.
- Risk Tolerance: Assess the potential fallout of compatibility issues to gauge how much risk you’re willing to shoulder.
- Costs vs. Benefits: Balancing the immediate resources saved against the long-term implications of forgoing thorough testing ensures you don’t save now only to pay dearly later.
In the realm of software development, every decision shapes the journey. When compatibility testing takes a backseat, proceed with eyes wide open, balancing innovation with the unwavering commitment to deliver a seamless user experience.
Types of Compatibility Testing
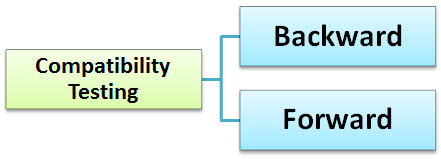
#1) Forward testing: makes sure that the application is compatible with updates or newer mobile operating system versions.
#2) Backward testing: checks whether the mobile app has been developed for the latest versions of an environment also work perfectly with the older version. The behavior of the new hardware/software has been matched against the behavior of the old hardware/software.
Read Also: 6 Types Of Software Testing Models
Compatibility type of testing can be performed on operating systems, databases, systems software, browsers, and mobile applications. The mobile app testing is performed across various platforms, devices, and networks.
Who is Involved in Compatibility Testing?
In the realm of software testing, various team members play key roles in conducting compatibility testing:
1. Developers:
In the design stage, developers evaluate the performance of applications on a particular platform. This platform could be the only release platform for this program. Developers concentrate on making sure that the application works well in this target platform.
2. Testers:
Quality assurance teams, whether internal or external, are involved in system-wide compatibility testing. Testers test the application compatibility across various devices, major operating systems, and browsers. They want to find and solve the possible problems that can happen in many environments.
3. Customers:
Insights from customers using hardware or configurations that have not gone through a rigorous testing process by the team are valuable. The experiences are then the first real benchmarks of specific layouts which may uncover incompatibilities otherwise missed through testing.
What is Tested in Compatibility Tests?
Compatibility testers typically assess various aspects of the software to ensure its seamless performance across diverse environments:
1. Performance:
Stability testing involves determining the stability of a program by assessing its overall responsiveness. This helps locate any incidents of system crashes on certain gadgets or platforms.
2. Functionality:
Compatibility testing verifies the standard characteristics and functionality of an application to determine its suitability for delivering quality outputs. For instance, a CRM may fail to offer back-end sales data or analytics for users running legacy operating systems.
3. Graphics:
This is where compatibility testing comes in, because it deals with some of the potential issues that may arise when displaying graphical elements on multiple browsers or devices. These checks ensure a functional program even on different screen resolutions.
4. Connectivity:
Compatibility tests look at how well the program interacts with the user’s device and its database, including detecting items such as printers. For example, such tests may show whether the app fails to communicate with its database over 4G networks.
5. Versatility:
Compatibility testing guarantees the adaptability of an application to both old and new versions of a given OS. Backward and forward compatibility tests allow ensuring the users to avoid lock out from a program because of an old version.
Process of Compatibility Testing
The compatibility test is conducted under different hardware and software application conditions, where the computing environment is important, as the software product created must work in a real-time environment without any errors or bugs.
Some of the main computing environments are the operating systems, hardware peripherals, browsers, database content, computing capacity, and other related system software if any.
The Initial Phases of Conducting Compatibility Testing are as follows:
- Define the platforms on which mobile app is likely to be used
- Create the device compatibility library
- Make a drawing of various environments, their hardware’s, and software to figure out the behavior of the application in different configurations
- Initiate a testing environment and start testing compatibility across multiple platforms, networks, and mobile devices. After noticing the behavior report any error or bugs detected and get them fixed.
- Again perform the testing by following the same process, till no bugs can be found.
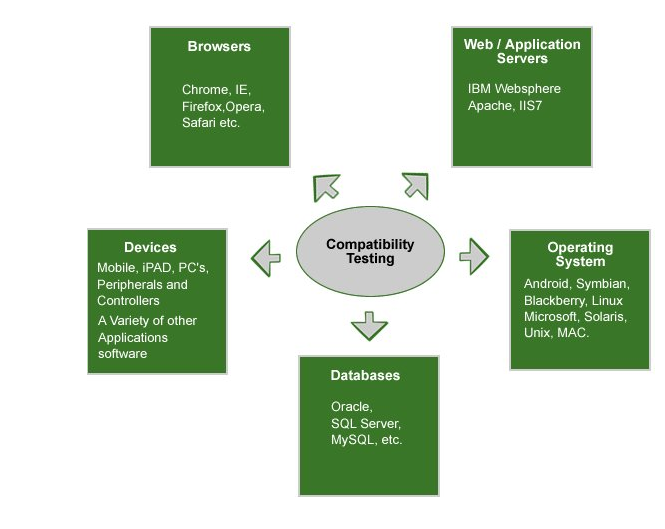
Categories of Compatibility Testing
- Hardware –To ensure compatibility across various hardware devices
- Operating system – To make sure that the software works equally across various OS’s
- Network – Software is tested with various fluctuating parameters of a network
- Devices – How the software is performing across various devices
- Versions – To check the compatibility across various versions of OS across devices backward and forward compatibility testing has to be performed
Advantages of Compatibility Testing
- Customer complaints can be avoided in the future
- Feedback in the testing stage will enhance the development process
- Apart from compatibility, scalability, and usability, stability will be revealed
- Makes sure that every prerequisite is set and agreed by the engineer and the client
- Ensures success in business
- Reputation and goodwill of the company will increase
Challenges of Compatibility Testing:
When companies engage in compatibility testing during software testing, they encounter several challenges including:
1. Limited Time:
Although the automation tools are quite efficient, compatibility tests should coincide with agreed development timeline by a company. It is rather hard for a team of testers to decide which devices and browsers should be used to ensure higher test coverage.
2. Lack of Real Devices:
Compatibility testing usually involves using virtual machines that mimic real devices, which is much cheaper and faster than buying actual components and platforms. But, this method may violate result integrity due to the fact that performance can vary in accordance with user interaction using actual devices.
3. Difficult to Future-Proof:
Since compatibility testing is confined to the current platforms, there is no guarantee that the application will work as intended under future Windows or Google Chrome operating systems. Solving problems after release is more expensive, and the application can potentially be rendered obsolete due to issues with compatibility.
4. Infrastructure Maintenance:
Many automated tests involve in-house testing across a number of platforms, especially mobile apps resulting in high infrastructure cost. Therefore, authenticating compatibility for mobile applications could require a set of real mobile devices that would provide consistency but at quite an expensive price, also requiring continuous replacement.
5. High Number of Combinations:
Compatibility tests comprise several elements, including operating systems, type of browsers and hardware versions in addition to firmware screen resolution. With enough time, even accommodating all the universal combinations is rather impossible. Compatibility and configuration tests should focus on the most common device combinations to achieve maximum coverage.
How To Do Compatible Testing?
Have a clear idea about the platform the app will be working on
The person and team involved in the process must have good platform knowledge
Set up the environment and before the actual test do a trial run.
Report the issues properly and make sure that it has been rectified. If you are finding new bugs make sure that after the rectification old fix is working fine.
Examples of Compatibility Test Cases and Scenarios:
Compatibility test cases provide the foundation for testing team’s strategy, which specifies inputs; testing strategies and expected outputs; these expected outputs are matched to actual results.
Because of the variety of devices and configurations that are included, this procedure is usually wide-ranging.
Common Compatibility Test Cases:
1. HTML Display:
Provide correct display of HTML web applications across different devices and media types.
2. JavaScript Usability:
Check the functionality and user-friendliness of the program’s JavaScript code.
3. Resolution Testing:
Compare the performance of your application at different screen resolutions.
4. File Directory Access:
Check the program’s ability to open and manage file directory.
5. Network Connectivity:
Verify that the application readily connects to all viable networks.
Specific Examples in Software Testing:
1. Social Networking App:
Validate the full functioning of a mobile app on iOS and Android devices on various device models.
Look into problems like animated GIF rendering on selected iPhone versions to guarantee uniform user experience.
2. Video Game:
Ensure the adaptability of graphical options in video games, such as screen resolution and UI scaling.
Work out problems, such as aliasing mistakes that will give nasty blurry graphics due to irregular graphic cards.
3. CRM Cloud System:
Evaluate the applicability of customer relationship management solutions with databases, especially those that use cloud storage.
Provide seamless functionality across various networks such as 3G and 4G for non-internet users.
Perform extensive testing on various operating systems, and sort out the bugs that appear only in certain platforms like Linux devices.
Tools For Compatibility Testing

Tools make the process much easier. Major tools used in the industry include,
Conclusion
The main intention behind performing testing is to make sure that the software is working fine in any kind of platform/software/configuration/browsers/hardware etc.
Testing compatibility will reduce the gross error of the software. Thus, this comparatively inexpensive process is a boon to ensuring that your product is a success.
There are some most common defects which can be found in the mobile application by the compatibility tester; Differences in the UI with respect to appearance and feel, issues with font size and alignment, concern with respect to Scroll Bar and marked changes in CSS style and color, issues like broken tables or frames, etc.
Testbytes overcomes challenges associated with this testing, like system integration, app distribution management, performance and security, platform, OS, and device integration, and the physical characteristics of mobile devices, etc., and offers comprehensive mobile app testing services.


 Software Testing Events
Software Testing Events App Testing
App Testing Web App Testing
Web App Testing Game Testing
Game Testing Automation Testing
Automation Testing Load Testing
Load Testing Security Testing
Security Testing Performance Testing
Performance Testing Hire a Tester
Hire a Tester