What is Exploratory Testing in Software Testing?
February 18th, 2019

Exploratory testing is a process where testers can be creative in exploring the software without knowing much about the working of the system. let’s dig deep
What is Exploratory Testing?
It is a testing approach where you explore the system and venture into those aspects and functionalities which may or may not directly affect the system’s outputs, in order to find underlying errors.
It is all about exploring the system, discovering hidden errors, investigating their cause, and rectifying them. There are no pre-defined test cases formed in exploratory testing and therefore the testers explore the system aimlessly in hopes to find unforeseen bugs.
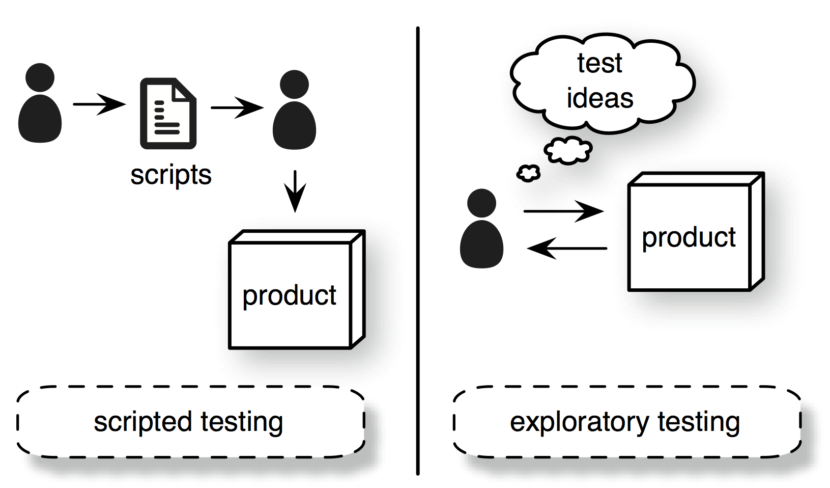
The purpose of performing exploratory tests is to learn more about the system and its functionality and using your existing knowledge about the system to find errors.
Testers need to be very creative and innovative in order to perform exploratory testing as the aim is to test the system for unexpected errors using unexpected techniques.
Even though there are no pre-defined test cases, testers may note down or document their ideas and things they want to test before performing the test.
Description of exploratory testing techniques?
There are different ways the process can be done. Based on that it can be divided into 3 main types as below:
- Freestyle Testing: As the name suggests, this is ad-hoc testing where-in each tester picks up a module or the entire application and randomly runs through the application. It is like a quick smoke test done to ensure everything is as expected.
- Scenario-based testing: In this type of exploratory testing, each tester picks up a user scenario and tests the application flows around that use case. They try to cover as many navigations, data permutations, and flow as possible to ensure the stability and functionality of that scenario.
- Strategy-based testing: This type of testing involves implementing the core testing methodologies into an exploratory test. In this test, the experienced tester would apply techniques like BVA (boundary value analysis), equivalence techniques, and more to the objects in the application.
How is functional exploratory testing different from structured exploratory testing?
1. Flow of the test
In structured testing, the flow of the test is directed by test cases that are prepared ahead of time.
Test cases are not determined in advance in exploratory testing and the flow is directed from exploring the system.
2. The objective of testing
The main objective of structured testing is to find foreseen errors whereas in exploratory testing the aim is to learn about the system and gain knowledge about its functionality.
3. Nature
Structured testing is predictive in nature as the flow of the test is predicted in advance.
Exploratory testing is spontaneous and investigative in nature. Tests are performed on a proper investigation is conducted.
4. The end results
The end results of structured tests are known and anticipated. However, the end results in exploratory tests are unknown and unexpected.
Wish to know about the types of software testing? Read here
When to use exploratory testing?
The process is mostly standalone and can not be used to confirm the quality of any software product, it is always used to supplement the other testings. Some of the situations where exploratory testing will be very fruitful and helpful are:
- To understand how the application works including the look and feel.
- In cases where the testing bandwidth is very crunched, exploratory testing may be performed on the least critical or rarely used modules of the application
- Check out the new features and changes in the application after each new release.
- To help new testers to understand the application, and also to test the application from a fresh perspective
- To supplement the structured testing towards the end of the testing phase
Exploratory Testing Process
1. Learning
This is the first step of exploratory testing and one which is very crucial. Learning about the system is important because you will be able to better analyze all the minor and major functionalities of the system and check it for bugs.
Your knowledge about the system will help you explore the system and create test designs and plans accordingly.
Unless you do not have knowledge about the system you will not be able to explore it in detail.
2. Test Design
Tests designs are created spontaneously during exploratory testing and there is no need for documentation of test cases, scripts and the conditions of the test.
3. Test Execution
Test execution is performed along with test designing. As soon as you plan and design your test you execute it without waiting for formal documentation. Only the key components of the test are recorded like the bugs that are detected or ideas for the next test.
4. Analysis
When some bugs are detected on exploring the system, proper analysis and feedback are made in order to rectify the errors.
The previous test result feedback helps testers to prepare for future tests and apply logical reasoning to guide the future of the software testing life cycle.
Advantages of Exploratory Testing
- During the process, there is no preparation time required before a test. It saves a lot of time and effort from the testers as they can focus solely on exploring and learning about the system rather than preparing test cases and documentation.
- It allows testers to find critical and hidden bugs and errors that cannot be found through formal testing approaches. All the bugs which do not directly affect the system outputs and get overlooked during initial testing can be detected through exploratory tests.
- The results of the previous tests help testers guide their future tests and explore the system in a better and more detailed way. This speeds up the testing process and testers are able to find more bugs easily.
- Exploratory testing helps testers gain in-depth knowledge about the system. When a bug is found they can learn its scope, size, nature, etc., and provide better solutions to the developers.
- When the system under test is intricate, complex, and vast, exploratory testing may generate better results and prove to be more efficient in finding bugs than formal testing techniques.
- When there is very little time for testing a system, exploratory testing is the best way to detect bugs quicker and in more efficient ways. Lots of time is saved when the documentation process is eliminated.
- The most significant advantage of exploratory testing is that it helps testers learn about the system. Testers are able to develop and test the system for different scenarios and get to know how the system will perform under such circumstances.
Disadvantages of Exploratory Testing
There are some disadvantages related to exploratory testing which make it a little harder to implement.
- The tests that are performed during exploratory testing are spontaneous and not documented which makes them hard to review and keep for future references.
- Since there is no documentation involved, keeping a track of the tests performed and the functionalities already explored is difficult.
- Repeating a test performed during exploratory testing the exact same way again is not possible. This is a huge disadvantage when you need to repeat a test to find a specific error found in a previous test.
-
Challenges in exploratory testing
There are some challenges in exploratory testing because it is not structured. Let us check out some of the major challenges:
- Issue Reproduction: once an issue is found, it may be difficult to reproduce it, since there are no defined steps that the tester followed. To avoid this tester would either enable recording in the device.
- No Exit Criteria: It is difficult to decide when to stop the testing as there are no defined tasks that need to be completed before concluding the tests.
- Uncertainty in test coverage: There are no defined documents or procedures to capture what is tested and what is not tested. Hence the test coverage can not be determined
- No defined metrics or reports: There are no formal metrics or reports to substantiate the amount of testing or the success of the testing activity. Many times it becomes a challenge to convince the management of the effort involved and the purpose.
Steps in exploratory testing
Exploratory testing does not follow a particular structure; however, there are a few steps that are common to each exploratory test. The preparation of exploratory tests is a 5 step process:
1. Learning and classifying errors
The first stage of exploratory testing is gathering the results of the previous exploratory test in order to learn the errors found in the past projects. Testers need to analyze these errors and understand the root causes of the bugs so that they can develop a test plan or strategy to test their system.
2. Test Charter tool
Test charter is a tool that is used to run exploratory tests. The stakeholders define the scope of the test and risks that need to be found using the test charter. Thus the charter should tell testers the following things:
- What tests should be performed
- How the system can be tested
- What risks should be focused on while exploring the system
3. Time Box
Time Boxing is the practice of setting a fixed amount of time known as a timebox during which a tester or a team of testers work together to find bugs. The time box session should not be interrupted and the testers should only focus on testing the system.
The testers working in pairs or groups can come up with the most creative exploration techniques and device efficient solutions to the errors found.
4. Analyzing the results
Once the testing process is completed, the results of the test are reviewed. The defects found are evaluated and testers learn the causes of the defects in order to come up with the best solutions.
5. Feedback
The results are compiled and compared with the charter. This helps testers identify whether they have tested the system according to the stakeholder’s needs and demands.
Things to keep in mind for exploratory testing
1. Understand the main aim of testing
Exploratory testing is all about learning about the system and understanding its core functionality by exploring unexpected system paths. During this process, certain unforeseen bugs are detected.
2. Planning the test is very important
Although test cases are not pre-defined during exploratory testing, it does not mean that exploratory tests are completely unplanned. Testers study the system and previous test results in order to figure out and plan their test. This helps them save a lot of time as they know what they are looking for.
3. This is skill-based testing
Testing skills are an essential part of exploratory testing. Testers completely rely on their skills in order to explore the system and test it for defects. Therefore exploratory testers should be highly skilled and have good knowledge of all software testing techniques.
4. Keeping a record of the test can be very beneficial
Even though exploratory tests are not documented, recording the findings, results, and defects found or any other outcomes of an exploratory test can be very beneficial.
5. Exploratory testing should be a team activity
It is always better to perform exploratory tests in pairs or in a team. This helps testers to come up with better test plans, exploration techniques, and solutions to the defects found.
Top 10 Ideas for exploratory testing

Wish to know about various QA methodologies? Read here
Example for Exploratory testing
The below image is an indication of how test cases are created for checking out the functionality of a web app.
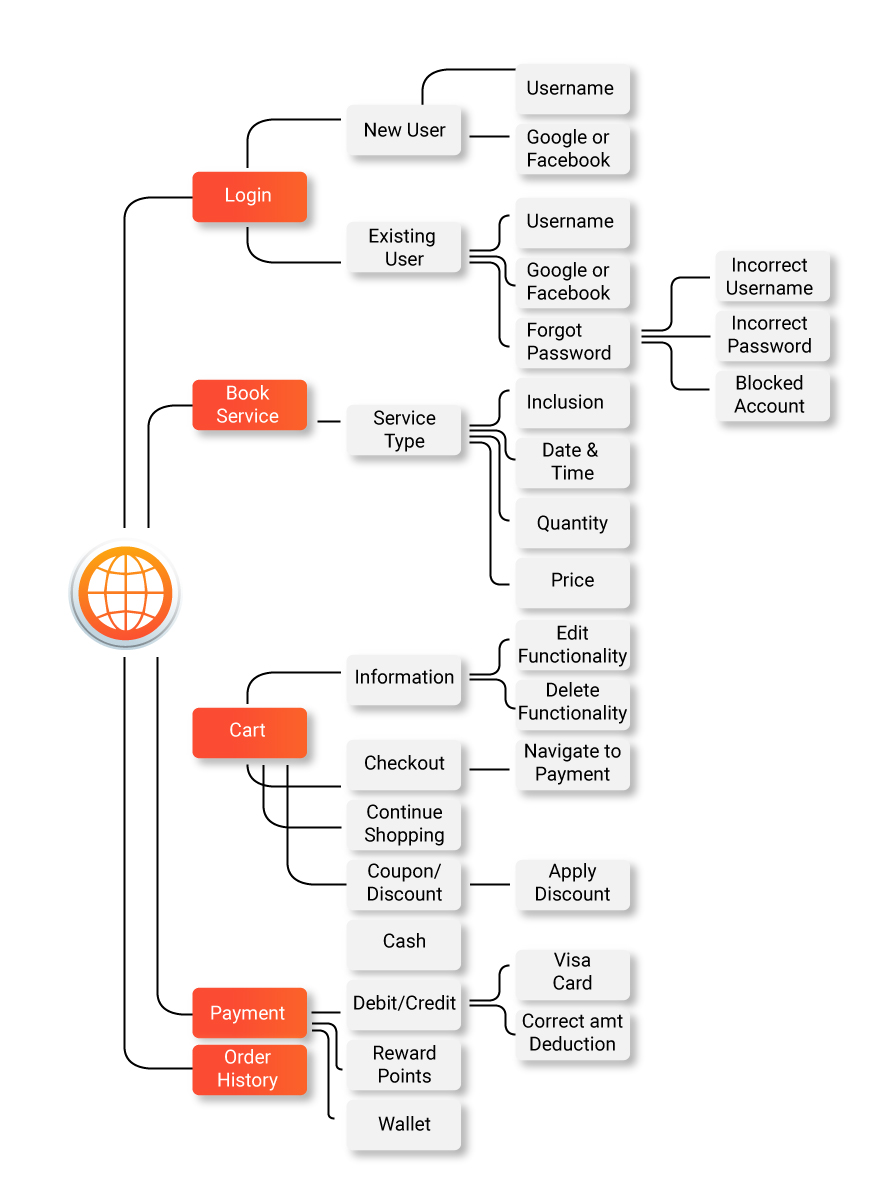
Exploratory testing documentation
- Keeping documented through notes is an effective way.
Eg: *NEW* /LIVE/ “Browser: Login with Gmailfirefox” (23-july-2021 09:44:20)
newUser@gmail.com
Client id = 357
https://mail.google.com/mail/u/0/#inbox
Login page displayed => OK
Previous account name displayed => OK
Login => OK
Logout Button available => OK
</OK>
- Mind Map style
You can use web-based tools such as XMind7 to document the process. The conventional mind mapping technique would not work in this case. Create all the test cases as nodes and can be saved into a template. Data such as environment, date, execution browser, time, the theme of the site, input data, environment, output data
Exploratory testing vs ad-hoc testing
|
Exploratory Testing |
Adhoc Testing |
|
Testing is carried out without much knowledge about the software but in a formal way |
Complete freedom in testing the software |
|
Documentation is mandatory |
Not that important |
|
Charter directed testing |
No particular plan |
|
Maximum test cases are executed |
No need for test cases |
|
Form of positive testing |
Form of negative testing |
|
Helps in learning the application |
Helps in developing innovative ideas in testing |
|
Does not need much time to commence |
Needs preparation time |
Conclusion
It overcomes all the shortcomings of structured testing. It helps testers detect errors that go unnoticed during scripted tests as they do not directly affect the outcome or working of the system.
This is the reason exploratory testing has become a very popular testing approach, especially for complicated systems. Exploratory testing has many advantages over scripted testing and helps testers focus on gaining knowledge about the system.


 Software Testing Events
Software Testing Events App Testing
App Testing Web App Testing
Web App Testing Game Testing
Game Testing Automation Testing
Automation Testing Load Testing
Load Testing Security Testing
Security Testing Performance Testing
Performance Testing Hire a Tester
Hire a Tester