What is Security Posture Assessment?
April 10th, 2023
An organization’s cybersecurity posture is assessed to make sure it is solid.
A posture assessment is one of several procedures that must be completed in order to advance the cybersecurity maturity level.
A company must have a strong cybersecurity system in place or else its security is at danger.
Most firms are now very concerned about data breaches, cyberattacks, and online dangers, therefore they are devoting time and resources to assessing their cybersecurity posture.
However, there are several cybersecurity techniques and providers accessible, which makes it challenging and confusing for a firm to choose one.
Before moving on, let’s take a closer look at the definition of posture evaluation.
 What is Security Posture Assessment?
What is Security Posture Assessment?
A Security Posture Assessment (SPA) is a thorough assessment of the entire security posture of an organization.
It entails examining and evaluating several facets of a company’s security procedures, policies, and practices in order to identify weaknesses, dangers, and potential areas for development.
An organization’s security controls, procedures, and tactics are evaluated in order to learn more about their efficacy and resilience.
It assists in identifying areas of vulnerability in the security infrastructure and offers suggestions for risk reduction, security measure improvement, and alignment with industry best practices and compliance standards.
Several areas may be assessed as part of a security posture assessment, including:
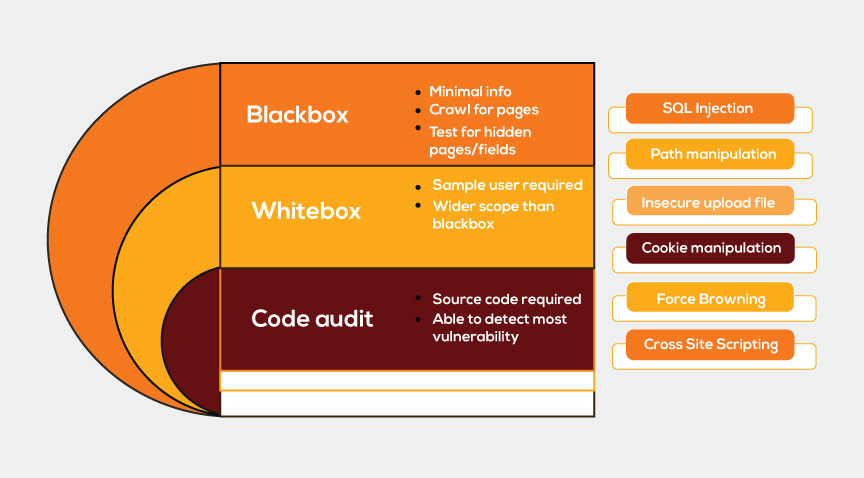
- Network security include examining the organization’s firewalls, routers, and other network components for holes in their setup, possible entry points for unauthorized users, and other vulnerabilities.
- System security is assessing the security settings and configurations of workstations, servers, operating systems, databases, and other crucial systems to spot weaknesses and possible security holes.
- Application security is the process of evaluating the safety of software, online, and mobile apps to spot weaknesses like poor input validation, weak authentication, or unsafe coding techniques.
- Analyzing physical access restrictions, security guards, surveillance systems, and other physical security measures to find gaps that might permit illegal entry or other breaches.
- Analyzing the organization’s methods for protecting data, such as data categorization, encryption, access restrictions, steps to stop data leaking, and backup and recovery processes.
- Reviewing the organization’s security policies, incident response plans, disaster recovery plans, and employee awareness initiatives to make sure they are thorough, current, and well stated. Security Policies and Procedures.
- Assessing the organization’s compliance with key security laws, industry standards, and regulatory requirements can help you find any gaps and make sure you’re in compliance.
- Evaluation of the efficiency of security awareness programs and training given to workers to make sure they have the information and abilities to adhere to secure practices.
A thorough report detailing the findings, vulnerabilities, and suggestions for enhancing the organization’s security posture is often produced after the evaluation.
The report may be used as a road map for putting security improvements into practice, for prioritizing remediation initiatives, and for boosting overall security resilience.
What are the different security postures?
Security postures describe the overarching strategy and mentality that an organization employs in relation to security. Several typical security postures are listed below:
Permissive Posture: In a permissive posture, companies put user comfort and ease of use ahead of strict security measures.
Users should be able to do their duties with the fewest limitations possible, which often leads to laxer security precautions.
This stance may be dangerous since it might make you more susceptible to intrusions and breaches.
Defensive: Taking a defensive stance places a significant emphasis on security procedures and controls that guard against possible dangers.
Multiple layers of security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, access restrictions, and encryption, must be put in place.
The emphasis is on limiting hazards and preventing illegal access.
Resilient posture: A resilient posture highlights the company’s capacity to tolerate and bounce back from security catastrophes.
It entails putting in place reliable backup and recovery systems, redundancy safeguards, and disaster recovery strategies.
The main objectives are to reduce downtime, ensure company continuity, and swiftly resume regular operations.
Agile Posture: Adopting an agile posture entails modifying security controls and procedures to keep up with quickly changing threats and technology.
It places a strong emphasis on adaptability and the capacity to act rapidly in the face of new security threats.
Continuous monitoring, threat information collection, and quick deployment of security updates and fixes are often components of this posture.
Risk-Aware Posture: Adopting a risk-aware posture is being aware of and skillfully handling security threats.
Organizations adopting this stance carry out thorough risk assessments, rank security expenditures according to risk categories, and put in place the necessary controls and mitigation techniques.
The emphasis is on striking a balance between risk management and corporate goals.
collaborative posture: A collaborative posture entails actively involving internal and external stakeholders in order to improve security.
It involves encouraging information sharing and cooperation with partners, developing a culture of security awareness, and integrating staff in security procedures and decision-making.
The goal is to instill security awareness within the company.
Organizations that value privacy rights and the protection of personal information adopt a privacy-focused stance.
This stance requires developing robust data protection safeguards, privacy policies, and consent processes in accordance data protection legislation like GDPR, LGPD, PIPEDA, and CCPA as well as industry-specific regulations like GLBA, FISMA, CPS 234, the NYDFS Cybersecurity Regulation, and HIPAA,
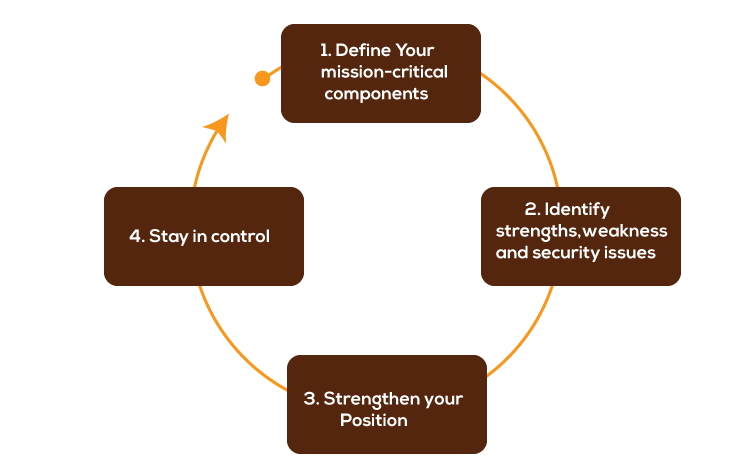
Strategy for improving Security posture assessment
For improving the posture, you should have a tool in place which can do the following:
- The tool you deployed must define your inventory inside the company.
- The tool must be able to screen all the IT assets for all significant risks, including phishing, obsolete or unpatched software, malware, SQL injection, and others.
- The tool should provide analytics from which to make references.
- A critical level for these flaws should be established based on the degree of vulnerability it introduces into the system.
- clearly state the security posture assessment’s goals. Identify the security infrastructure, policies, and procedures that need evaluation and improvement. To monitor progress, set quantifiable objectives and success criteria.
- Make sure the evaluation addresses all pertinent security topics, such as network security, system security, application security, physical security, data security, and compliance needs. Gather information by using a mix of automated tools, manual testing, interviews, and documentation reviews.
- Following a posture assessment, the system should be constantly monitored for new vulnerabilities.
- Create a dedicated staff that will routinely maintain a security posture evaluation. If a certain crew will be looking at it, maintenance will be simple.
- Participate important stakeholders in the evaluation process. This comprises the IT staff, the security teams, the management, the legal and compliance teams, and other pertinent departments. Their participation and cooperation will provide insightful information and aid in identifying important areas for development.
- Utilize well-established security frameworks and standards, such as the CIS Controls, ISO 27001, or the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. These frameworks give best practices for putting security controls in place and offer a systematic method for evaluating security postures.
- Make sure the assessment report contains concise, doable suggestions for correcting found weaknesses and vulnerabilities. Give best practices, instructions, and comprehensive processes for remediation. Adjust the advice to the organization’s unique situation, resources, and competencies.
- Create a thorough remediation plan that specifies the procedures, deadlines, and accountable parties for carrying out the suggested security changes. Set goals, assign resources, and prioritize projects to keep track of.
- Consider hiring outside security consultants or experts to undertake impartial analyses and provide unbiased viewpoints. The efficacy of the evaluation may be increased by the specific expertise, experience, and impartial viewpoints of outside specialists.
- Promoting a solid security culture among the staff may go a long way toward preventing these occurrences. Employee awareness and education can help them to avoid clicking on harmful links, which will help to reduce the frequency of phishing assaults.
Planning a strategy for robust posture assessment
You should know how to have an effective strategy for making your system more robust and cyber-attack defensive.
The security posture assessment professionals have a very difficult task on their shoulders. They must establish the priorities of attacks that need to be dealt with first.
You should always know how to manage and mistake in case any cyber-security risk comes into your organization. Proper governance and having proper cyber-security programs in the organization will make sure that how planning a strategy is important.
It is always to identify the sensitive information because safeguarding them at any cost should be a part of our strategy. IT teams should regularly perform vulnerability scanning, phishing simulations, and penetration testing to minimize security thefts and increase the posture assessment level.
There are different frameworks for improving posture assessment. OCTAVE is one of the frameworks which is widely used.
It is an operational critical threat, asset and vulnerability evaluation which is useful for an organization that knows the major gaps and know how to fill these.
Another framework is FAIR which means Factor analysis of information risk. Last is the NIST RMF framework which should be implemented in case you avoid the first two frameworks due to compatibility issues. Risk assessment is a mandatory step in all the three frameworks and continuous assessments are a core part of the cyber-security level analysis.
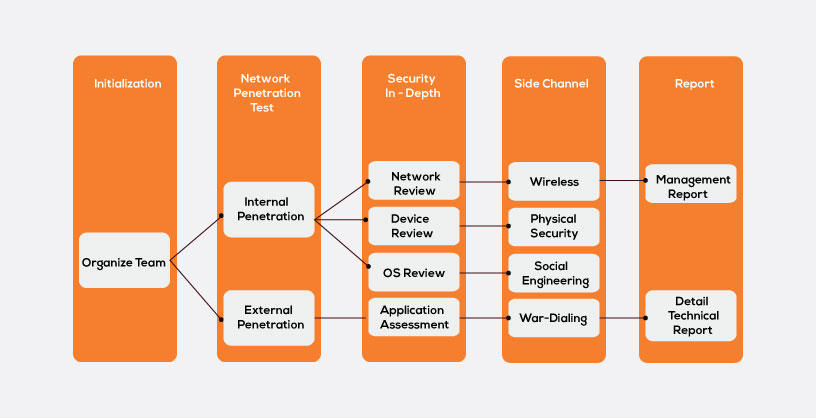
Phases involved in Security posture assessment
Planning Phase: Validating the scope of the assessment, resource identification, stakeholders identification, developing a work-plan, etc. happens in this phase.
Documentation review: All the documents that are required to commence testing will be reviewed in this phase.
Assessment: Internet exposure, on-site audit, findings, analysis and -defining cyber-security posture will be carried over in this phase
Reporting: All the deliverable will be listed in the report
When does your company need a cybersecurity posture assessment?
- If you wish to know the current status of the cybersecurity
- For implementing correct and mandatory cybersecurity measures
- If you wish to have a detailed analysis to check on the vulnerabilities
- Your company defensive system against cyber attacks is not up to the mark
- if you wish to get ROI on you cybersecurity measures
- If there is any kind of integration happening
Tips to improve your cyber-security posture
- Have a real-time updatable inventory of the IT assets of your company
- Continuous monitoring of IT assets and expose the system to planned cyber and see how the defensive mechanism is
- Analyze the result and do a proper risk assessment and mark the vulnerability points
- Once improved start from the first periodically

Conclusion
So, we learned how the organization used to ignore these threats and that lead to a drastic loss.
To safeguard your data and maintain cybersecurity have a robust and high-level cybersecurity posture assessment in place.
This is going to act as a barrier for your product, assets, and organizations. Start making your strategy today and make your organization risk free.


 Software Testing Events
Software Testing Events App Testing
App Testing Web App Testing
Web App Testing Game Testing
Game Testing Automation Testing
Automation Testing Load Testing
Load Testing Security Testing
Security Testing Performance Testing
Performance Testing Hire a Tester
Hire a Tester